|
Photo credits : oceaneye
- manta trawl and microplastic samples Scientific
agenda
The passive igloo participates in different scientific collaborations.
This page is intended to serve as a platform for information
on completed or ongoing activities. For more information,
please get in touch.
The
passive igloo - a sailboat dedicated to science
The passive igloo offers accomodation to master
students and researchers motivated by an interest and passion
towards research in the Arctic regions, whether sailing in
the summer or during Arctic winter where the vessel is stationary
in the ice.
Scientific partners 2020
University of Rome - GREAL, University of Geneva-
Department F.-A. Forel, Faculty of Science, University of
Savoie Mont-Blanc - LCME, IFSTTAR and Nantes - GERS and the
National Georgaphic Society of Italy






Scientific partners 2018
In collaboration with not-for-profit organisation
PolarQuest2018 : Centro Fermi, Istituto Nazionale di Fisica
Nucleare, Consiglio Nationales delle Ricerche, CERN the European
Organization for Nuclear Research, Geographic research and
Application Loboratory, Centro di Ricerca, Sviluppo e Studi
Superiori in Sardegna, National Georgaphic Society of Italy



Scientific partners 2015 - 2017
Météo-France, Oceaneye, Ifremer,
University of Brest, University Savoie Mont Blanc. Topics
of study cover weather, climate, biodiversity and pollution
of the oceans. The passive igloo is also involved in Isaaffik,
a new gateway connecting Arctic research, education, consultancy
and logistics.




Scientific agenda
Nanuq2020
: the Blosseville coast inventory

A scientific expedition to the east coast of Greenland
Building unique knowledge for environmental science
Scientific program :
- Modelling a portion of the Blosseville coastline
from georeferenced photographs
- detailed modeling of different sectors from orthophotos
(UAVs)
- documentation of thermal areas by infrared thermography
(UAV)
- documentation of vegetation indices obtained by
NDVI camera (UAV)
- inventory of fauna and flora on selected areas
(transects)
- salinity profiles to determine the thickness of
the fresh water/melting water layer (DST probe)
- temperature profiles, search for underwater hot
springs (DST probe)
- our sonars will enable us to carry out bathymetry
of certain sectors (3D sonar)
- study of dissolved methane in freshwater lakes
(sampling)
- reconnaissance of freshwater lakes in preparation
for 'Flying Plastics 2021' (Universities of Paris
and Savoie)
Location: Blosseville coast (east coast of Greenland);
the exploration of Scoresby Sund will be made in the
perspective of prospecting for future projects
When: July - August 2020
|
| |
PolarQuEEEst : Extreme Energy
Events - CERN



Built by school students from Switzerland, Italy,
Iceland and Norway at CERN, PolarQuEEEst is a special
detector to catch cosmic rays coming from the distant
regions of our universe. Three of these special “telescopes”
will be built to measure the cosmic ray flux at different
latitudes, with one of them on board Nanuq and the
two others installed in the schools of the students
from Italy and Norway who will build them.


Capteur EEE installé sur le pont avant de Nanuq;
membre d'équipae Ombretta PInazza en train
de préparar le capteur pour l'installation
en Islande
The project is part of the Extreme Energy Events
– Science Inside Schools (EEE) project coordinated
by the Museo storico della Fisica e Centro Studi e
Ricerche Enrico Fermi (Centro Fermi), an Italian research
institute with its headquarters in the historic building
of the old Institute of Physics in via Panisperna
in Rome, where Enrico Fermi made his famous studies
on the importance of slowing down the neutrons to
produce induced radioactivity.
Publications:
Abbrescia M. et. al. (EEE Collaboration), "
New high precision measurements of the cosmic charged
particle rate beyond the Arctic Circle with the PolarquEEEst
experiment", The European Physical Journal C
volume 80, Article number: 665, 2020 (PDF)
Nania R., Pinazza O., "Measuring cosmic ray
showers near the north pole with the extreme energy
events project", Il Nuovo Saggiatore, volume
34, 2018
CERN Courier, International Journal of High-Energy
Physics, "Cosmic research poles apart",
December 2018
|
| |
Arctic
Micro- et Nano-plastics : CNR - ISMAR

Plastics make up the largest quantity of the non-biodegradable
material contaminating the world’s oceans and
is a huge environmental concern because its longevity
means that it can be distributed over huge distances
from its origin, and accumulate in remote areas such
as the Poles. Once in the ocean, mechanical and biological
processes cause plastics to break down into microplastics,
which are difficult to remove from the ocean and are
a threat to the diverse marine food webs and ecosystems
supported by polar waters.

Using the Mantanet to collect microplastic
data samples in the Arctic.
Water samples were collected using a manta net in the
top 16 cm of surface water.
Supported by 
Publications :
Aliani S. and al, "Polarquest2018 expedition :
Plastic Debris at 82°07 North" in Mare Plasticm
- The Plastic Sea, Springer, 2020
|
| |
PCB's
in atmosphere : LCME, University of Savoie

Laboratoire Chimie Moléculaire et Environnement
(LCME)

During the second leg of the expedition, Svalbard’s
circumnavigation, Polarquest2018 will drop scientific
coordinator Frédéric Gillet will travel
from King's Bay out to scientifically-interesting glaciers.
During his mission, he will install special sensors
that have to be in place for a sufficiently long time
in the environment to obtain significant results in
measuring the quantity of PCBs in the air. They will
be recovered in one or two years’ time.

Frédéric Gillet deploying
the passive sensor to dose atmospheric PCBs, far away
from the pollution of civilization (photo Alwin Courcy)
Links :
|
| |
Polar
Drones : Geographic Research and Application Laboratory

Polarquest2018 will test the use of commercial low
cost minidrones as scientific tools for field research
in the Arctic.
Our drone team will deploy a fleet of three small drones
(two mini-drones below 2 kgs of max take-off weight,
one micro-drone, below 300 grams) in several scenarios
on the coast around the Svalbard archipelago, above
78 degrees N latitude. Mini and micro drones are especially
suited for efficient and low-cost survey of remote and
typically inaccessible areas such as the Svalbard archipelago,
both on land and sea environments.
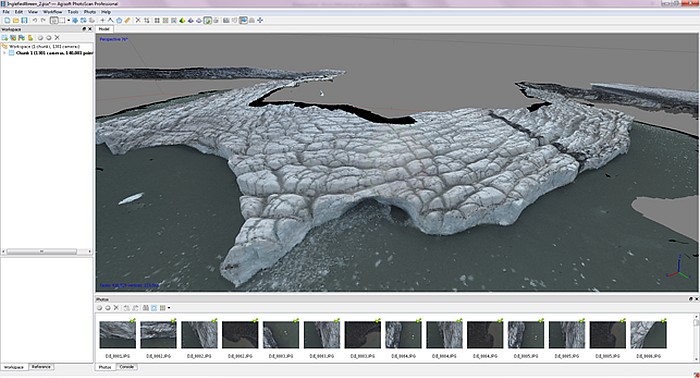
Exemple de rendu de modèle 3D
du survol de InIglefieldbreen sur la côte orientale
du Spitzberg (image Gianluca Casagrande)
We will carry out observations of ice-cover variations
(comparing with archived data), land conditions, vegetation,
floating ice distribution and presence and behavior
of fauna, including polar bears. Surveys will include
photogrammetry, photo/video footage in the visible light
as well as multispectral and thermal imagery to be used
in different types of analyses.
The objective of this campaign is to develop efficient
and cost-effective observation methods.
Links :
|
| |
Climate and Weather : Météo-France

In order to improve the quantity and quality of atmospheric
data collected from across the globe, scientists seek
to maximize the number of measurements, especially
at sea. These data include improving weather forecasts
and safety at sea.


Deployment of SVP drifeter buoys, Nanuq Greenland
2015 (photos Alain Berthoud)
"SVP drifter data buoys" collect and transmit
data via satellite:
The goal is to deploy additional drifting weather
buoys on different areas during the trip. In parallel,
the boat will be equipped with an integrated weather
station that will provide a complete data set at each
full hour via Iridium SBD. These data can be viewed
in near real time.
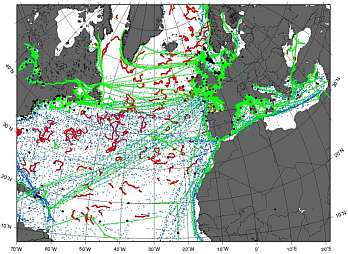
Chart : air pressure observations
over the sea surface in November 2013, red dots =
drifting buoys, source EUMETNET
Web : http://www.eumetnet.eu
|
| |
Arctic
micro-plastics : Ifremer / Oceaneye



Carte : modèle
de prédiction numérique de concentration
de débris plastiques flottants. Source: Maximenko
et al. (2012)
Five huge waste zones about the size of a country
float on the ocean surface. They are called the seventh
continents or waste patches, accumulation areas. They
are mainly composed of small plastic debris from fragmentation
of waste. The cause of their existence is human pollution
that is transported by ocean currents. This phenomena
is now no longer a hypothesis but a scientific certainty.
The objective is to determine the quantity of plastic
contained in the sea water along the voyage.
Web : http://www.oceaneye.eu |
| |
Maritime
microorganisms : University of Brest



Niskin bottle and work in progress on board, Nanuq Greenland
2015 (photos Sylvie Margot)
a) Diversity of microorganisms:
The structure, function and biodiversity of Arctic
marine ecosystems are influenced by several key factors
and are very well adapted to the extreme conditions
of their environment. However, impacts of climate change
on Arctic ecosystems are expected to be very strong
and more rapid than any other biome on earth. As phytoplankton
is the basis of many food webs, it is absolutely crucial
to study their spatial distribution and diversity. Moreover,
there are concerns that the nature of algae blooms in
the Arctic could be modified, especially due to the
sea- ice retreat, or ocean acidification. It is proposed
to investigate phytoplanktonic diversity by sampling
regularly along the cruise line, with an emphasis around
the coast of Greenland.
b) Macronutrients (nitrates, phosphates and
silicates)
In the Arctic, important shifts in nutrient availability
took place in recent years. As a result, significant
changes in primary production of Arctic Ocean waters
occurred. As complementary measurements to microorganisms
diversity, nutrient distribution will be investigated
along Nanuq voyage, with a focus on total dissolved
inorganic nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon.
c) Trace Elements
Phytoplankton growth requires carbon, light and macronutrients).
In addition, trace elements play a key role : some are
essential for living organisms (e.g Fe, Mn , Cu, Ni
, Zn , Co), while others are toxic (eg Pb and Hg). The
structure, function and biodiversity of marine Arctic
ecosystems may be affected by any bioavailability variation
of these trace elements. Their distribution is tightly
linked to the variation of their inputs, such as sea-ice
or melting glaciers.
The goal is to quantify some trace elements (total
dissolved mercury and particulate Fe, Mn, Al) in different
areas along the voyage, with an emphasis around Greenland
Web : http://www-iuem.univ-brest.fr |
| |
PCB's
: University Savoie Mont-Blanc

Laboratoire Chimie Moléculaire et Environnement
(LCME)

By means of passive sensors, polychlorinated biphenyls
(PCBs) will be sampled in the atmosphere and in the
ocean on behalf of the LCME of Savoie Mont Blanc University.
The laboratory analysis of these molecules captures
in passive sensors will determine the concentrations
of gaseous PCBs in air and PCBs dissolved in water and
then calculate PCB flows at the air-water interface.


S etup of passive absorbers (water - left; air - right),
Nanuq Iceland 2015 (photos Alain Berthoud)
These calculations will clarify the role of the ocean
with respect to these persistent organic micro: source
or sink of atmospheric PCBs. Comparison with data previously
acquired by other teams by scientists from concentrations
measured in the Arctic air will finally provide information
on the atmospheric dynamics of these pollutants in the
current context of climate change.
- PCBs in water
- PCBs and PAHs in air
Laboratory analysis of these molecules captured in
passive absorbers made it possible to determine the
concentrations of gaseous PCBs in the air and PCBs dissolved
in seawater, and then to determine their diffusion modes.
This work was presented at the 16th International Conference
on Chemistry and the Environment in Oslo, ICCE 2017.
Poster:
 clic
to zoom clic
to zoom
Abstract...
Web : http://www.lcme.univ-savoie.fr |
| |
Energy
: The passive igloo project
The 'passive igloo' is
the cabin of a 60' polar expedition sailboat. The design
is inspired by concepts and techniques used in low-energy
high performance buildings.
The aim is to pass through an arctic winter in a self-sufficient
way and without the use of non-renewable energy in order
to explore how simple and robust constructive and technical
solutions may to challenge low-cost energy scarcity
in a credible way. Transposed to temperate climates,
the experience feedback will be useful to outline the
habitat of tomorrow.

The real passive igloo - end of winter, Nanuq Greenland
2016 (photo Peter Gallinelli)
Measured variables:
- indoor air temperature: living area (floor, ambient,
ceiling), cabins, buffer zone
- inner and outer surface temperatures and heat flux
trough the thermal envelope of the igloo
- indoor air quality : relative humidity and CO2
levels
- air change rate
- energy produced, consumed
- occupancy rate, activities
- external environment: temperature, relative humidity,
solar radiation, wind speed
Scientific purpose : to observe and describe the comfort/energy
ratio, document comfort and hygrothermal operation and
establish a detailed energy balance.
Web (internal links) :
|
|